Pytorch3d 使用笔记
基础知识
pytorch3d的默认距离单位是m(米)
坐标系是 ??
https://pytorch3d.org/docs/why_pytorch3d
api
https://pytorch3d.readthedocs.io/en/latest/modules/index.html
tutorials
https://pytorch3d.org/tutorials/
https://pytorch3d.readthedocs.io/en/latest/overview.html#tutorials
github
https://github.com/facebookresearch/pytorch3d
光源:Lights
pytorch3d中存在三种光源 分别是
- 点光源
PointLights - 平行光源
DirectionalLights类似太阳光 - 环境光源
AmbientLights
PointLights
点光源是一种具有位置和强度的光源,光线在所有方向上发射,并以固定的衰减率远离光源。在 PyTorch3D 中,PointLights 类提供了创建和管理点光源的功能,可以通过设置位置、强度和颜色等属性来控制点光源的效果。
PointLights(ambient_color=((0.5, 0.5, 0.5), ),
diffuse_color=((0.3, 0.3, 0.3), ),
specular_color=((0.2, 0.2, 0.2), ),
location=((0, 1, 0), ),
device: Union[str, torch.device] = 'cpu')
"""
ambient_color – RGB color of the ambient component, 环境光
diffuse_color – RGB color of the diffuse component, 漫反射光
specular_color – RGB color of the specular component, 镜面反射光
location – xyz position of the light. 光源位置, 单位米(m)
device – Device (as str or torch.device) on which the tensors should be located
"""
DirectionalLights
平行光源是一种无限远的光源,光线在同一方向上发射,并且不会随距离的增加而衰减。
类似于太阳光。
DirectionalLights(ambient_color=((0.5, 0.5, 0.5), ),
diffuse_color=((0.3, 0.3, 0.3), ),
specular_color=((0.2, 0.2, 0.2), ),
direction=((0, 1, 0), ),
device: Union[str, torch.device] = 'cpu')
"""
direction: 光的方向向量
"""
AmbientLights
环境光是一种无处不在且强度均匀分布的光,模拟了来自场景中各个方向的多次反射和散射的光线,用于模拟整体的背景照明。
AmbientLights(*, ambient_color=None, device: Union[str, torch.device] = 'cpu')
"""
ambient_color: 环境光的颜色,默认为白色,可以用来生成纯色的mesh, 取巧的话,可以当mask
"""
https://pytorch3d.readthedocs.io/en/latest/modules/renderer/lighting.html
## 相机:Cameras
pytorch3d中目前有四种相机模型, PerspectiveCameras, OrthographicCameras, FoVPerspectiveCameras, FoVOrthographicCameras。此外还有鱼眼相机 FishEyeCameras
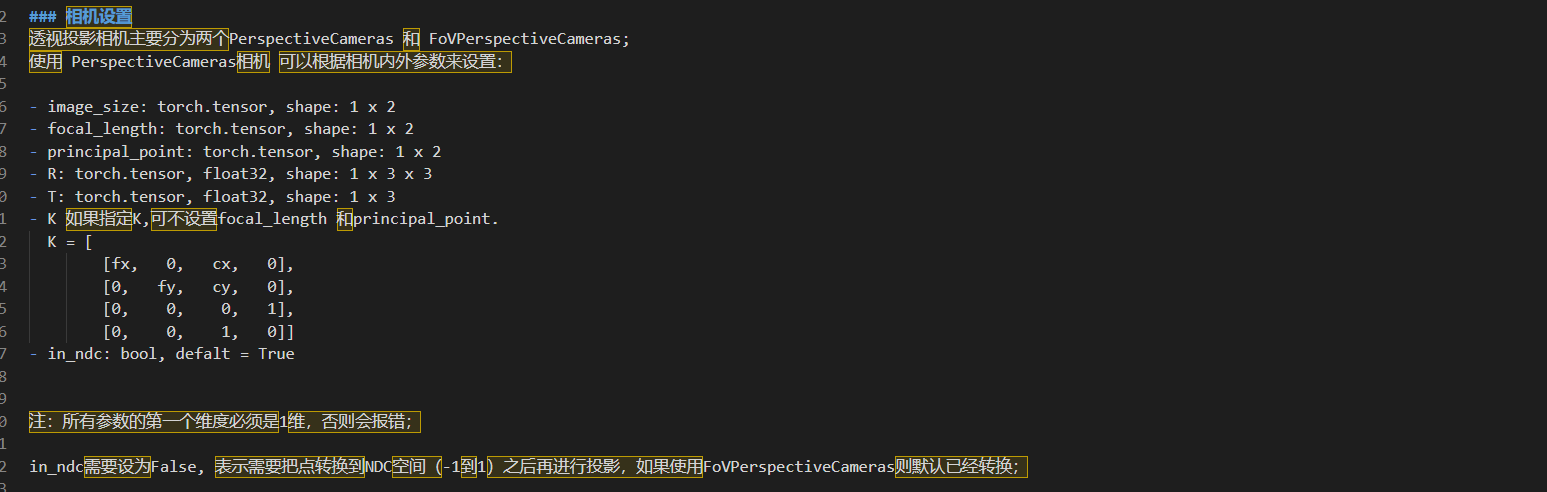
PerspectiveCameras
透视相机模型,之前叫SfMPerspectiveCameras,常用的模型之一,opencv中常用,用来得到和图像对应的渲染图
hf_w = img_w / 2
hf_h = img_h / 2
# 需要变换下相机的fx, fy, px, py
fx = 229.869 / hf_w
fy = 229.19 / hf_h
px = (324.828 - hf_w) / hf_w
py = (240.32 - hf_h) / hf_h
cameras = PerspectiveCameras(device=self.device, focal_length=((fx, fy), ), principal_point=((px, py), ))
fx = focal_length[:, 0]
fy = focal_length[:, 1]
px = principal_point[:, 0]
py = principal_point[:, 1]
K = [
[fx, 0, px, 0],
[0, fy, py, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 1],
[0, 0, 1, 0],
]
FoVPerspectiveCameras
FoV透视相机模型, 之前叫OpenGLPerspectiveCameras,常用的模型之一,和opengl的设置参数一致
cameras_ = PerspectiveCameras(...)
k_ = cameras_.get_projection_transform().get_matrix()
cameras = FoVPerspectiveCameras(K=k_, device=self.device)
OrthographicCameras
该相机模型生成的是正交投影(orthographic projection),即平行投影。正交相机将场景中的物体投影到图像平面时,保持了物体在深度方向上的尺寸不变,不受距离的影响。
fx = focal_length[:,0]
fy = focal_length[:,1]
px = principal_point[:,0]
py = principal_point[:,1]
K = [
[fx, 0, 0, px],
[0, fy, 0, py],
[0, 0, 1, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 1],
]
FoVOrthographicCameras
FoV正交模型,
该相机模型在 OrthographicCameras 的基础上增加了视场角(Field of View, FoV)的设置。视场角表示了相机在场景中能够看到的角度范围,从而控制了生成图像中可见的物体数量。通过调整视场角的大小,可以改变生成图像中的透视效果和可视范围。
因此,FoVOrthographicCameras 提供了在正交相机模型中调整视场角的功能,允许用户根据需求控制生成图像的透视效果和可视范围,而 OrthographicCameras 则不包含视场角设置。选择使用哪种相机模型取决于应用场景和需求。
# 将mesh归一化后可以使用
cameras = FoVOrthographicCameras(
device=self.device,
znear=0.1,
zfar=10.0,
max_y=1.0,
min_y=-1.0,
max_x=1.0,
min_x=-1.0,
scale_xyz=((1.0, 1.0, 1.0), ), # (1, 3)
)
look_at_view_transform
重新放置一个相机,返回相机外参R, T. 这是相对世界坐标系来说的。
# 常见用法
https://pytorch3d.readthedocs.io/en/latest/modules/renderer/cameras.html?highlight=look#pytorch3d.renderer.cameras.look_at_view_transform
"""
dist: 相机距离物体的距离,单位m
elev:以度数或弧度表示的角度。上下旋转
是从物体到相机的矢量与水平面 y = 0(xz 平面)之间的角度
azim:以度数或弧度表示的角度。左右旋转
从物体到相机的向量被投影到水平面 y = 0 上。
azim 是投影向量与参考平面(水平面)上 (0, 0, 1) 处的参考向量之间的角度
degrees: 控制角度单位为度数或弧度,默认为True, 表示用度数
还有其它参数可选
"""
R, T = look_at_view_transform(dist, elev, azim)
cameras = FoVPerspectiveCameras(device=device, R=R, T=T)
https://pytorch3d.org/docs/cameras
https://pytorch3d.readthedocs.io/en/latest/modules/renderer/cameras.html
https://pytorch3d.readthedocs.io/en/latest/modules/renderer/fisheyecameras.html
渲染:Rendering
sigma = 1e-5 # 可以改善grid 现象
raster_settings = RasterizationSettings(
image_size=(self.img_sz_h, self.img_sz_w),
blur_radius=np.log(1. / 1e-4 - 1.) * sigma,
faces_per_pixel=50,
)
blend_params = BlendParams(sigma=1e-4, gamma=1e-4, background_color=(0, 0, 0))
renderer = MeshRenderer(rasterizer=MeshRasterizer(cameras=cameras, raster_settings=raster_settings),
shader=SoftPhongShader(device=self.device, cameras=cameras, lights=lights, blend_params=blend_params))
# 只渲染Silhouette mask
renderer = MeshRenderer(rasterizer=MeshRasterizer(cameras=cameras, raster_settings=raster_settings),
shader=SoftSilhouetteShader(blend_params=blend_params))
https://pytorch3d.org/docs/renderer_getting_started
着色器:shader
TODO …
材质:materials
https://pytorch3d.readthedocs.io/en/latest/modules/renderer/materials.html